The Life of Stars
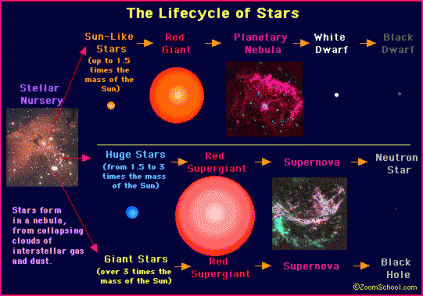
This page is about the birth, life, and death of stars, and all the different paths it can take.
Birth
Stars are thought to be born in nebulas.Nebulas are clusters of burning gas and dust. When gravity pushes in on the gas it gets denser and denser, eventually it is dense enough to burn it's own gas and becomes a star.
Life of Sun-like Star
Some stars start out being about the size of our sun and up to 1.5x larger (though scientests have recently found a star 10x bigger see space news) . They stay that way for a few billion years.
Red Giants
When sun-like stars get a little older, they expand into a Red Giant (the sun has about 5 billion more years before that happens.).These stars are cooler than they were before (you can tell because they are red.)
Plantery Nebulas
When a Red Giant starts to burn away its outer layer, it gets blown off and forms a Planetary Nebula. All that's left is the core (see White Dwarfs).
White Dwarfs
Eventually the star blows off it's outer layer (see Plantary Nebula) and all that's left is the burning center. It is now called a White Dwarf. These stars are some of the densest. A star that is the same size as the Earth is about 200,000 times as dense. A white dwarf star called Lucy is home to the largest known dimond, at its very core.
Black Dwarfs
At the very end of its life a star goes dark (like a light bulb) and ends up as a Black Dwarf. There are currently no known Black Dwarf stars in the Universe.
Life of Huge Stars
This is about the life of stars 1.5 to 3 times larger than the sun.
Red SUPERGiant
When a huge star is older it expands into a Red Supergiant. It is almost exactly like a Red Giant but bigger.A Giant Star also turns into a Red Supergiant. Really, that's all that it is, basically a bigger Red Giant.
Supernovas
When a Red Supergiant gets older, it colapses on itself and explodes. It leaves a cloud of dust and gas called a Supernova Remnent
Neutron Star
I don't really understand this that well, but I will give it my best shot.When a star goes through a Supernova once again all that's left is the core (to see what I mean by "once again" see White Dwarfs). Eventually the core collaspes under pressure and the electrons and protons cancel each other out and turn into netrons (thus Netron Stars). These are the densest stars, much denser than White Dwarfs. One teaspoon of a star would weight one billion tons on Earth.
Life of Giant Stars
This is about the life of stars 3 or more times the size of our sun. Almost the whole life of Giant Stars is the same as with Huge Stars, except they don't turn into Neutron Stars.
Black Holes
When a Red Supergiant explodes in a Supernova it colapses on itself and turns in to a Black Hole. A Black Hole is so large that not even light can escape its great gravitational force.
